This article provides a comprehensive guide to distinguishing between Fumed Silica and Precipitated Silica. It details their different production processes, unique properties including physical parameters and surface structure, and compares their performance and main application areas.
Silica, also called silicon dioxide( SiO₂) , is a white amorphous powdery substance. According to different production processes, silica can be divided into Fumed Silica and Precipitated Silica.
Fumed silica can be divided into Hydrophilic Fumed Silica and Hydrophobic Fumed Silica.
Fumed silica is an amorphous silica product made by high temperature hydrolysis of halosilanes.
SiCl₄ + H₂ + O₂ → SiO₂ + HCl
CH₃SiCl₃ + 2H₂ + 3O₂ → SiO₂ + CO₂ + 3HCl + 2H₂O
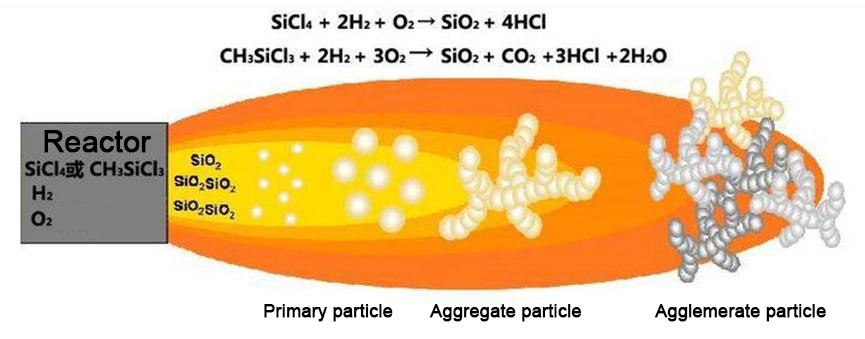
Its unique synthesis principle gives it a distinctive structure and excellent performance. Fumed silica is a multifunctional additive with reinforcing, thickening, antiprecipitation, matting, etc.; in general, fumed silica is divided into Hydrophilic Fumed Silica and Hydrophobic Fumed Silica products.
High temperature resistance
Non-combustible
High electrical insulation
Primary particle size: 7-40mm
Specific surface area: 50m2/g-400m2/g
SiO₂ content: 99.8%
In rubber, plastics, glue coating, adhesives, industrial catalyst, food, medicine, CMP and heat insulation and thermal insulation materials and many other fields are playing a vital role, and thus known as the best of the silica, favored by the market.
Precipitated silica, also called Precipitated Hydrated Silica, is made of quartz sand, soda ash, industrial sulfuric acid, etc., and the main component is SiO₂. The properties of precipitated silica are similar to those of carbon black, and the appearance is a white, highly dispersed amorphous or flocculent powder.
It is insoluble in water and most acids, soluble in caustic soda and hydrofluoric acid.
It is chemically stable. High temperature resistance is not easy to decompose and does not burn.
Higher electric margin.
Higher dispersibility, porous and larger specific surface area.
Higher reinforcing properties.
Primary particle size: Below 0.3um
Relative density: 2.319-2.653
Melting point: ≤ 1750°C
Additives for rubber tires, paints, toothpaste, etc.
Fumed Silica: Generated generally by hydrolysis of silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄) by reaction with hydrogen and oxygen at high temperature, which belongs to the fumed method; the by-product is HCl.
Precipitated Silica: Precipitated Silicoa is usually prepared by the sol-gel method, which means that solid precipitated Silicon Dioxide is obtained by the reaction of Sodium Silicate (Na₂SiO₃) and Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) in the aqueous phase to produce silicic acid, and then aging, precipitation, drying and other steps to obtain solid precipitated silica.
Fumed Silica | Precipitated Siliba | ||
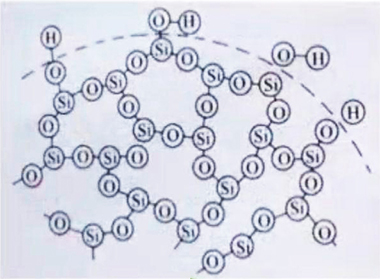 | 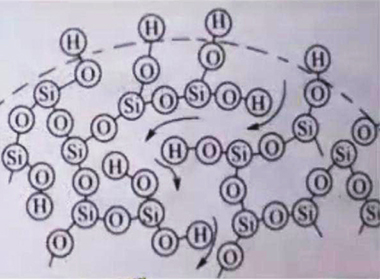 | ||
|
| ||
| Fumed silica | Precipitated Silica | |
| Particle size | 7-40mm, agglomeration occurs, strong adsorption capacity, particle size can become larger. | < 0.3um |
| Number of silicon hydroxyl groups | Hydrophilic Fumed silica: 2-3 | About 6 |
| Fineness | 1000 mesh or more | 300-400 mesh |
| Specific surface area | High (100-400 m²/g) | Lower (30-200 m²/g) |
| Surface Structure | Amorphous, three-dimensional structure with pronounced branched chains | Some pore structure, loose flocculent |
| SiO₂ Content | > 99.8 % | > 95.0 % |
| Impurity Content | < 2000 ppm | < 50000 ppm |
| Dispersibility | Easier to form agglomerates, dispersion requires additives | Relatively easy to disperse |
| Fumed silica | Precipitated Silica | |
| Dispersing properties | Difficult to disperse, requires high shear or ultrasonic dispersing equipment | Easier to disperse, can be added directly to water or slurry systems |
| Transparency | Suitable for high-transparency systems | Mostly used for opaque systems |
| Thickening/thixotropy | Strong thixotropic effect (a small amount is sufficient) | Better thickening but not as effective as the vapor phase method |
| costs | High cost (due to complex process, high energy consumption) | Low cost (simple process, common raw materials) |
| Main applications | Grease thickener, transparent adhesive thickening, coating rheology modifier, electronic materials, optical field, etc. | Rubber fillers (e.g. tyres), toothpaste rubbers, pesticide carriers, paint fillers, etc. |
For both types of silica, the right product can be selected according to the specific application scenario. Fumed silica has high performance and purity, and is correspondingly expensive; Precipitated silica, due to its low price, is suitable for use in products that are mass-filled and cost-sensitive.
Contact: Tony Li
Phone: +86-13263299644
Tel: +86-13263299644
Email: sales@ecoviaet.com
Add: No 3 Youyi Road,Tangshan,Huantai,Zibo,China
We chat
